Summary
Gas는 이더리움 네트워크에서 트랜잭션을 처리하기 위해 지불해야 하는 수수료를 의미합니다.
Description
Gas는 이더리움 네트워크에서 트랜잭션을 처리하거나 스마트 계약을 실행하기 위해 지불해야 하는 수수료를 의미합니다. Gas는 네트워크의 자원을 사용하는 대가로, 트랜잭션의 복잡성과 연산량에 따라 소비됩니다. Gas의 주요 특징은 다음과 같습니다:
- 수수료: Gas는 이더리움 네트워크에서 트랜잭션을 처리하거나 스마트 계약을 실행하기 위해 지불해야 하는 수수료입니다.
- 가변성: Gas 비용은 네트워크의 혼잡도와 트랜잭션의 복잡성에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
- 보상: 채굴자 또는 검증자는 트랜잭션을 처리하고 블록을 생성함으로써 Gas 수수료를 보상으로 받습니다.
Gas의 주요 요소
- Gas Limit: 트랜잭션이 소비할 수 있는 최대 Gas 양을 나타내며, 사용자는 트랜잭션을 전송할 때 Gas Limit을 설정할 수 있습니다.
- Gas Price: 사용자가 지불할 의사가 있는 Gas의 가격을 나타내며, 이는 Gwei 단위로 표시됩니다.
- Gas Used: 트랜잭션 실행 시 실제로 소비된 Gas 양을 나타냅니다.
Gas의 중요성
- 네트워크 자원 관리: Gas는 네트워크 자원의 효율적인 사용을 보장하며, 불필요한 트랜잭션을 방지합니다.
- 보안: Gas는 네트워크에 대한 공격을 방지하고, 스마트 계약 실행 시 무한 루프와 같은 문제를 방지합니다.
- 경제적 인센티브: Gas 수수료는 채굴자와 검증자에게 경제적 인센티브를 제공하여 네트워크의 안정성을 유지합니다.
https://ethereum.org/ko/developers/docs/gas/
PREREQUISITES
To better understand this page, we recommend you first read up on transactions and the EVM
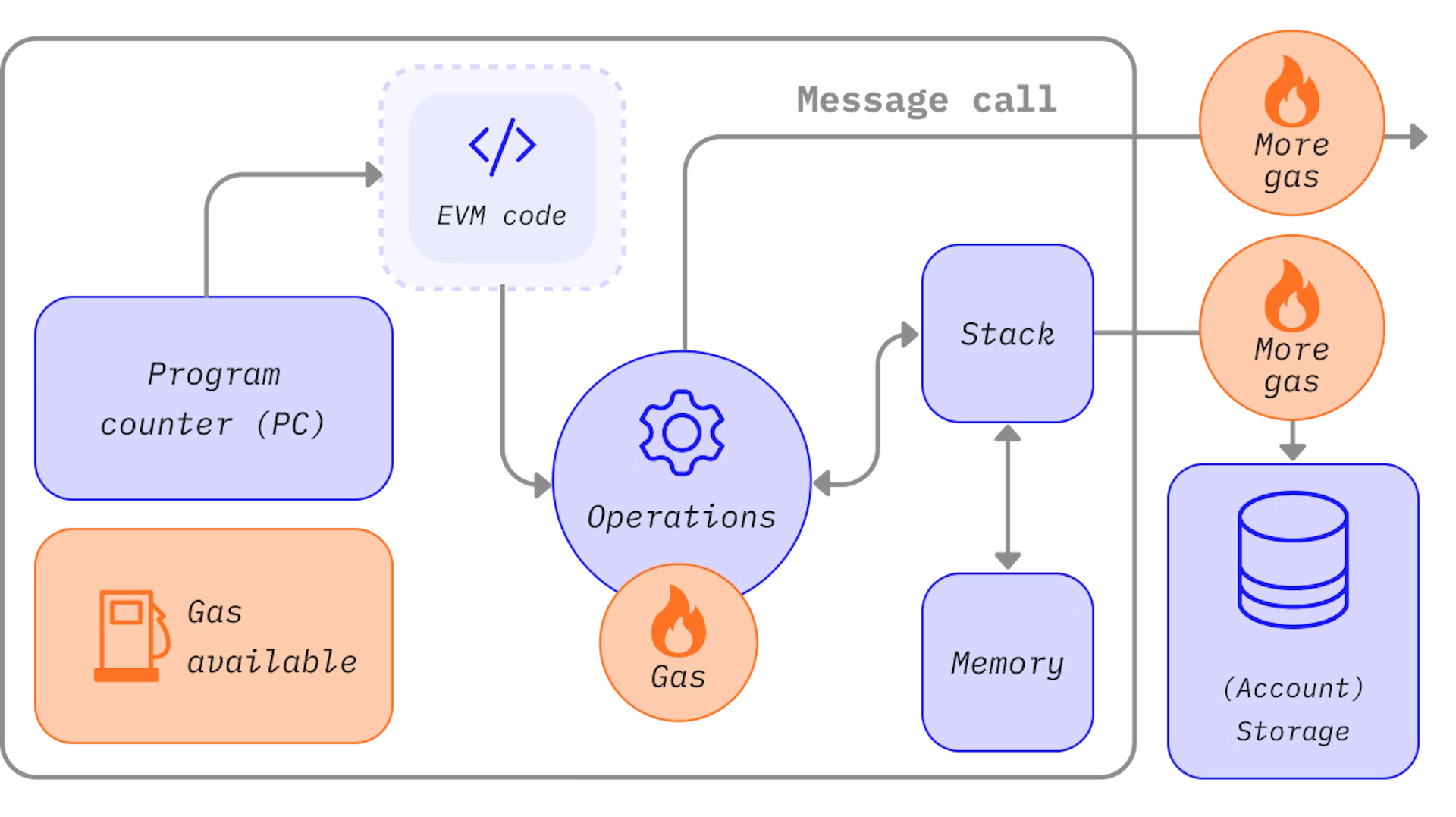
Ethereum gas
수수료
- Every transaction on Ethereum requires a small form of payment to process
- These fees are known as ‘gas’ fee
- Gas fees are not set, they change based on network congestion
How do I pay less gas?
Time your transactions
Just like travelling off-peak is less crowded and more affordable, Ethereum is generally cheaper to use when North America is asleep. (GPT에게 물어본 결과, KST 기준 오후 1시에서 7시 사이라고 한다)
Wait for gas to go down
Gas prices go up and down every twelve seconds based on how congested Ethereum is. When gas prices are high, waiting just a few minutes before making a transaction could see a significant drop in what you pay.
레이어 2 사용
Layer-2 chains are built atop Ethereum, offering lower fees and handling more transactions. They’re a good choice to save on fees for transactions that don’t need to happen on the main Ethereum network.
What causes high gas fees?
Whenever the amount of computation (gas) on Ethereum exceeds a certain threshold, gas fees begin to rise. The more the gas exceeds this threshold, the quicker gas fees increase.
Higher fees could be caused by things like popular decentralized apps (dapps) or NFTs, periodically increased trading on DEXs, or an overwhelming number of user activity at peak times.
Developers on Ethereum should take care to optimise their smart contracts usage before deploying. If lots of people are using a poorly written smart contract, it will consume more gas and could inadvertently cause network congestion.
따라서 효율적인 스마트 컨트랙트를 작성하는 능력이 중요하다.
Want to dive deeper? Check out the developer docs.
Attack of the Cryptokitties
In November 2017, the popular CryptoKitties project was launched. Its rapid spike in popularity caused significant network congestion and extremely high gas fees. The challenges posed by CryptoKitties accelerated the urgency of finding solutions for scaling Ethereum.
Why do we need gas?
Gas is a critical element in keeping Ethereum secure and processing transactions. Gas helps in many ways:
🪪 Gas keeps Ethereum sybil-resistant by preventing malicious actors from overwhelming the network with fraudulent activities. 개인이 익명의 다수로 변장하여 거짓된 활동을 하는 것을 억제한다.
💸 Because computation costs gas, spamming Ethereum with expensive transactions, either accidentally and maliciously, is financially disincentivized. 비용을 통해 무분별한 스팸을 억제할 수 있다.
⏳A hard-limit on the amount of computation that can be done at any one time prevents Ethereum from being overwhelmed, helping to ensure the network is always accessible. Opcode 별로 가스가 부여되기 떄문에, 한 번에 수행할 수 있는 연산량을 제한함으로써 네트워크의 부하를 예방할 수 있다.
How is gas calculated?
The total gas fee you pay is made up of a few parts:
- Base fee: a fee set by the network that has to be paid for a transaction
- Priority fee: an optional tip to incentivise node operators to include your transaction
- Units of gas used***: remember we said gas represented computation? More complex actions, like interacting with a smart contract, use more gas than simple ones, such as sending a transaction.
- * See Figure 1 to see how much gas different types of transactions use
| Transaction type | Units of gas used |
|---|---|
| Sending ETH | 21,000 |
| Sending ERC-20 tokens | 65,000 |
| Transferring an NFT | 84,904 |
| Swapping on Uniswap | 184,523 |
Figure 1: Gas used by transaction type
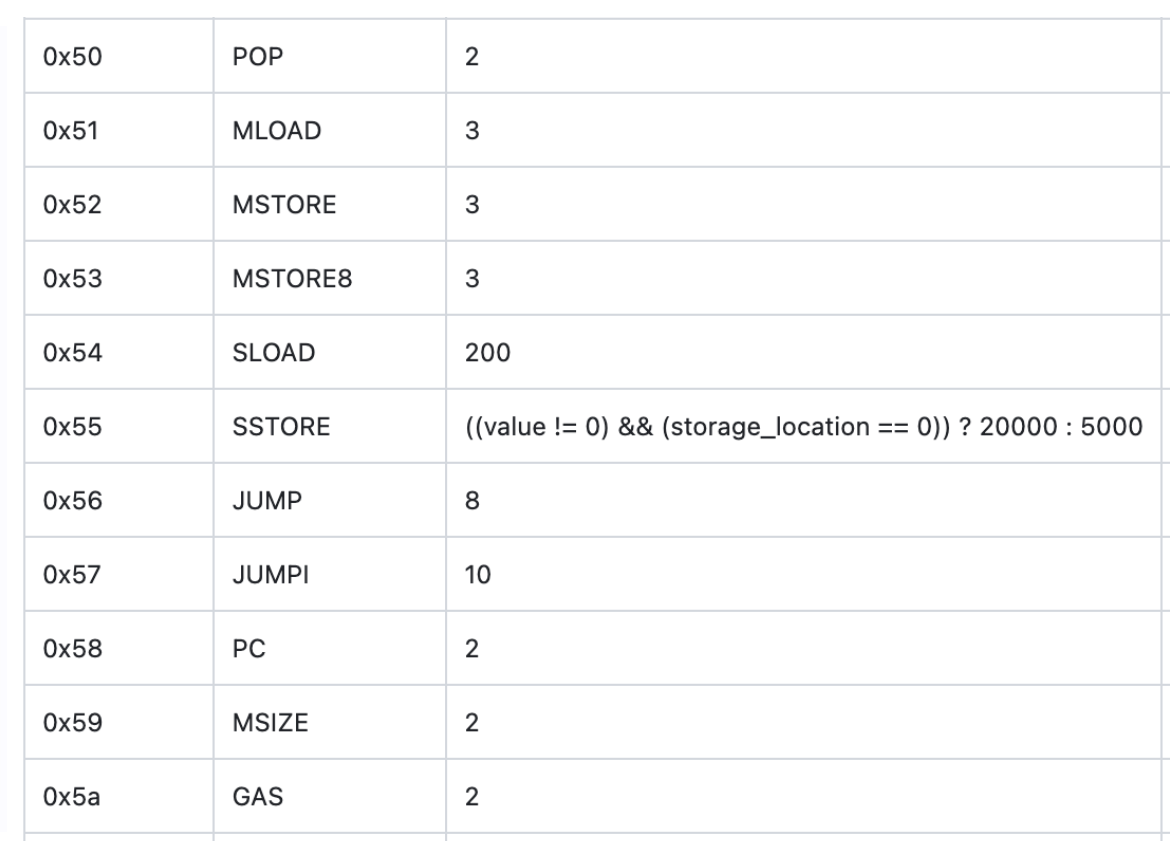
Opcode gas cost
Who gets paid the gas fee in my transaction?
Do I need to pay gas in ETH?
What is gwei?
Suggestions
레이어 2 사용
Layer-2 chains are built atop Ethereum, offering lower fees and handling more transactions. They’re a good choice to save on fees for transactions that don’t need to happen on the main Ethereum network.
Dapps are applications built on Ethereum. Dapps are disrupting current business models and inventing new ones.